问题描述(难度中等)
Sort a linked list in O(n log n) time using constant space complexity.
Example 1:
1 | Input: 4->2->1->3 |
Example 2:
1 | Input: -1->5->3->4->0 |
方法一:递归归并排序
记录下时间复杂度分析吧,如何理解归并排序的时间复杂度。假设当前有m个数字待排序,需要被分成logm次,每个同等级的子问题需要m的时间去排序。总体的复杂度为m*logm。
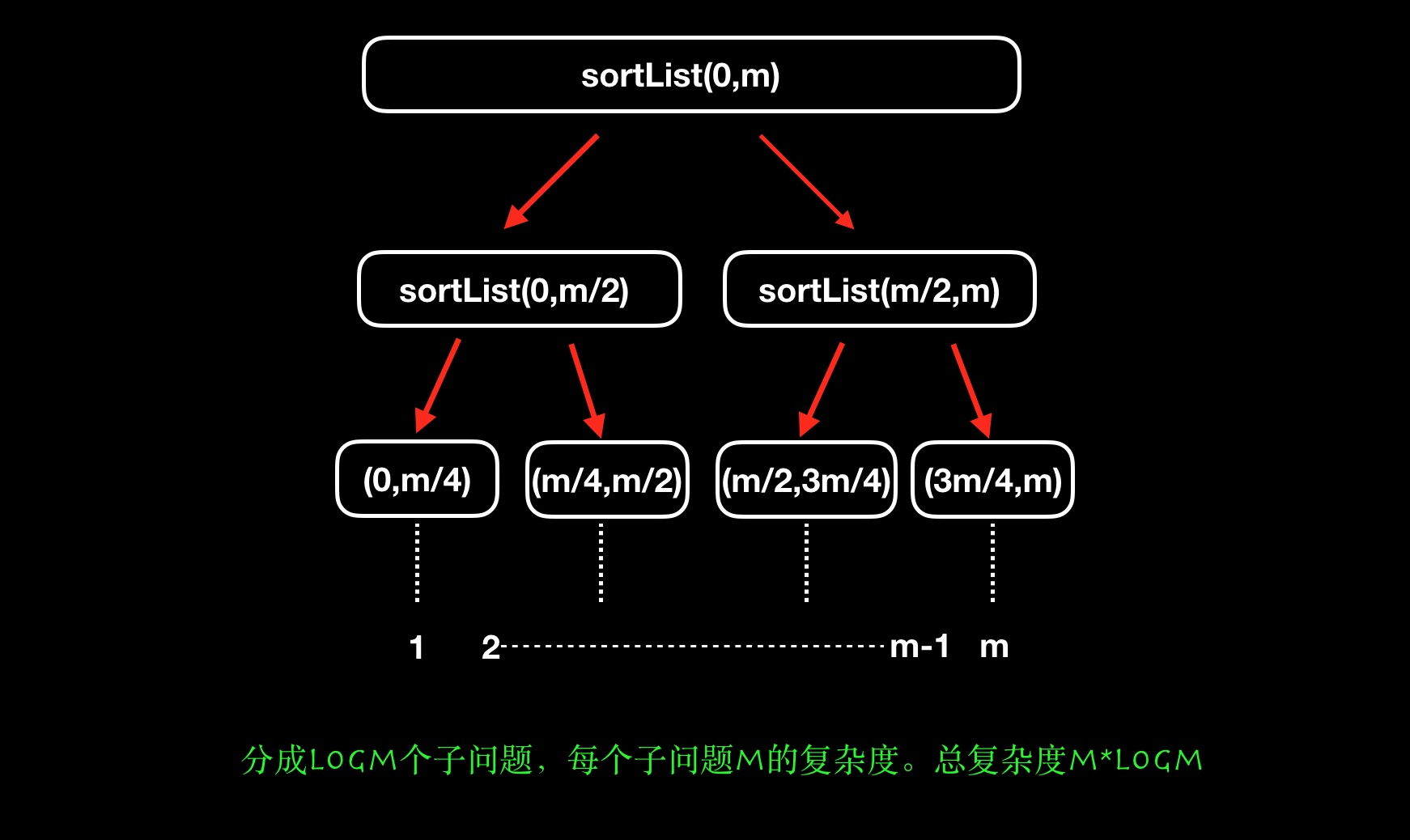
延伸一下,大文件排序,如果1024M(m)的文件,内存只有8M(n)。计算一下时间复杂度。
- mlog(m/n)+(m/n)nlogn,即mlogm。
1 |
|
总结
归并排序,递归排序,充分利用了递归的美感。